JAVA¶
一. JUC¶
-
AQS
-
CountDownLatch
-
CyclicBarrier
-
ReadWriteLock
-
Semaphore
-
Exchanger
二. 单例模式¶
- 饿汗式
public class SingleObject{
private static final SingleObject INSTANCE = new SingleObject();
private SingleObject(){}
public static getInstace(){
return INSTANCE;
}
}
- double checked
public class SingleObject {
private volatile static SingleObject singleton;
private SingleObject (){}
public static SingleObject getSingleton() {
if (singleton == null) {
synchronized (Singleton.class) {
if (singleton == null) {
singleton = new Singleton();
}
}
}
return singleton;
}
}
三. 引用类型¶
-
强引用 内存不够内存溢出¶
// -Xms20M -Xmx20M
public static void main(String[] args) {
byte[] bytes = new byte[1024 * 1024 * 20];
System.out.println(bytes);
}
// Exception in thread "main" java.lang.OutOfMemoryError: Java heap space
-
软引用 内存不够被回收¶
// -Xms20M -Xmx20M
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {
SoftReference<byte[]> softReference = new SoftReference<>(new byte[1024 * 1024 * 10]);
System.out.println(softReference.get());
System.gc();
TimeUnit.MICROSECONDS.sleep(500);
System.out.println(softReference.get());
byte[] bytes = new byte[1024 * 1024 * 10];
System.out.println(softReference.get());
}
//[B@574caa3f
//[B@574caa3f
//null
-
弱引用 GC 发生被回收¶
// -Xms20M -Xmx20M
public static void main(String[] args) {
WeakReference<byte[]> softReference = new WeakReference<>(new byte[1024 * 1024 * 10]);
System.out.println(softReference.get());
System.gc();
System.out.println(softReference.get());
}
//[B@574caa3f
//null
ThreadLocal
- key应用存在内存泄漏用虚引用解决
-
value还是存在内存泄漏,ThreadLocal用完需要删除对象
-
虚引用 获取不到值 使用场景堆外内存¶
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {
ReferenceQueue<byte[]> queue = new ReferenceQueue<>();
PhantomReference<byte[]> softReference = new PhantomReference(new byte[1024 * 1024 * 10], queue);
while (true) {
Reference<? extends byte[]> poll = queue.poll();
if (poll != null) {
System.out.println("gc 通知");
}
}
}
四. 线程¶
public enum State {
NEW, // 线程初始化,没有启动
RUNNABLE, // 可运行状态 1. running 2.Read
BLOCKED, // 被阻塞 synchronized
WAITING, // 等待唤醒 o.wait() t.join() LockSupport.park() Lock.lock()
TIMED_WAITING // 等待时间唤醒 Thread.sleep(time) o.wait(time) t.json(time)....
TERMINATED; // 线程结束
}
- 可见性,有序性 ,原子性
五. 线程池¶
\(N_{threads}=N_{cpu} *U_{cpu} * (1 + W/C)\)
预估线程= cpu核数 使用率(1 + 等待的时间/计算的时间)
2 = 1 * 100% *(1+0.5/0.5)
-
ThreadPoolExecutor¶
-
corePoolSize
- maximumPoolSize
- keepAliveTime
- TimeUnit
- BlockingQueue
- ThreadFactory
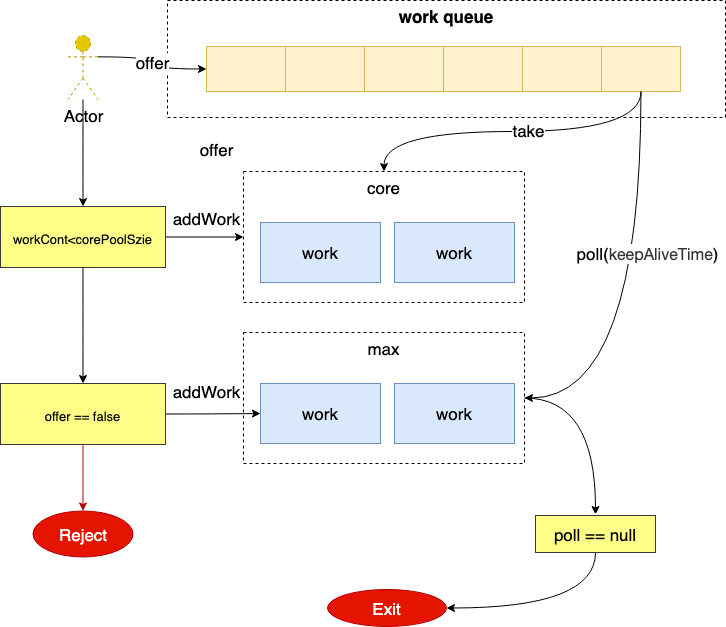
-
RejectedExecutionHandler
- Abort: 抛异常
- Discard:扔掉
- DiscardOldest:扔掉排队时间最久的
- CalleRuns:调用者处理任务
-
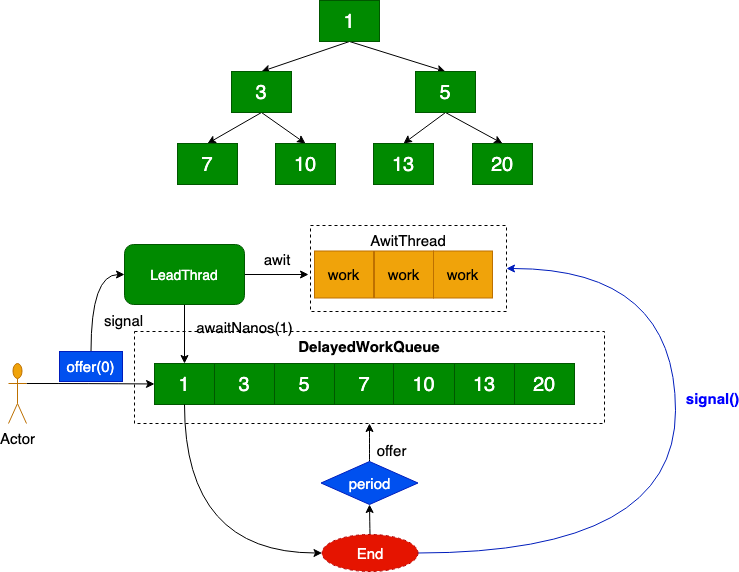
SheduledThreadPollExecutor¶
左孩子的索引是 2*n+1
右孩子的索引是 2*n+2
父节点的索引是 (n - 1) / 2
-
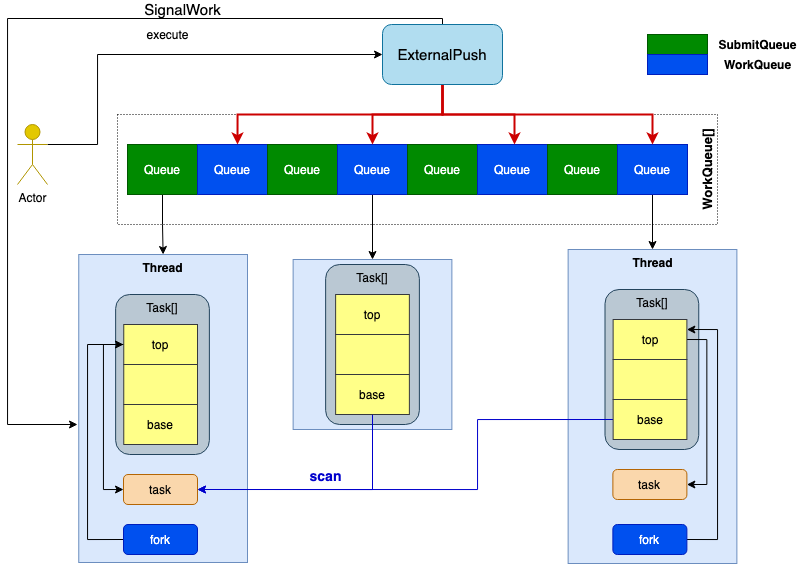
ForkJoinPool¶